-
Email Us
draktiwari@ymail.com
Email Us
April 14, 2025
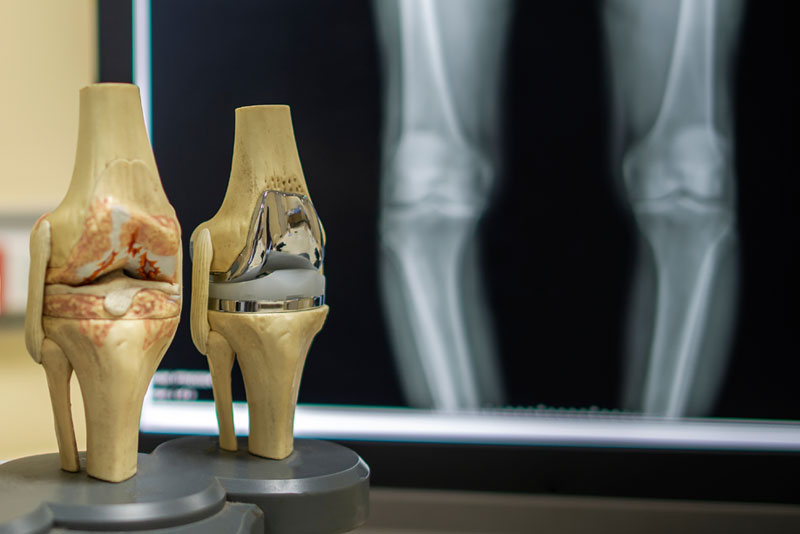
Knee replacement surgery is often utilized and proven to be effective in treating patients with chronic knee pain due to injury or arthritis. It restores quality of life, function, and mobility when the other interventions are ineffective. But maybe one of the most questioned questions by the patients is: “Should I have a partial or total knee replacement?”
As orthopaedic surgeons, it is imperative to advise the patients on how partial and total knee replacement are different in an effort to make them make sound decisions based on their individual condition, age, lifestyle, and long-term ambitions.
The paper examines the key differences, indications, recovery periods, complications, and results of both procedures.
To learn about the two surgical procedures, it is essential to know the general anatomy of the knee. The knee joint is separated into three compartments:-
If only one of the three compartments is involved in the arthritis or degeneration, a partial knee replacement might be adequate. If all three are involved, a total knee replacement is typically indicated.
A total knee replacement (TKR), or total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure where the three knee compartments are resurfaced. The procedure involves:-
It is the most performed knee replacement procedure and suits best for individuals who have extreme arthritis, notable deformity, or multiple injuries in the knee’s compartments.
Partial knee replacement, or unicompartmental knee replacement, is a procedure in which only the defective compartment of the knee is replaced. The rest of the joint, including its ligaments (such as the ACL and PCL), cartilage in the unaffected compartments, and bone structure, remains unchanged.
There are three partial knee replacements:-
PKR is the ideal choice for patients with osteoarthritis confined to a region, stable knees, and a normal body weight.
| Characteristic | Partial Knee Replacement | Total Knee Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| Length of Surgery | Only one compartment replaced | All the compartments of the knee replaced |
| Surgical Intrusiveness | Less intrusive, shorter incision | More intrusive, longer incision |
| Hospitalization | 1-2 days (same-day discharge) | 2–4 days |
| Recovery Time | Faster, usually in 4–6 weeks | Full recovery in 8–12 weeks or more |
| Pain & Swelling | Less post-op pain typically | More initial discomfort |
| Functionality | More natural feel and range of motion | Good pain relief, but less natural feel |
| Longevity | 10–15 years | 15–20+ years |
| Ideal Candidate | Early-stage arthritis patients | Advanced-stage arthritis patients |
| Cost | Typically lower overall cost | Higher due to hospital stay and surgery |
But be careful since PKR is not suited for all. If arthritis has the potential to worsen in other compartments in the future, then it could be a revision for total knee replacement.
While more recuperation is required with TKR, generally it is the best option for patients with a great deal of joint damage.
Partial or total knee replacement is a decision best made following extensive examination by an experienced orthopaedic surgeon. The decision makers are:-
Both procedures need a formal rehabilitation program. Recovery from partial knee replacement tends to be quicker, though. Most patients are able to return to normal activity in 4–6 weeks and can go back to low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or cycling in a few weeks.
Total knee replacement, though, needs a longer period of recovery. It may take patients 3–6 months to regain strength, balance, and mobility. Both procedures need physical therapy.
Surgeon skill, implant quality, and patient adherence to rehab regimens determine long-term success with both procedures.
Both total and partial knee replacement are great alternatives for those with knee arthritis, but whether the use of either should be decided to suit each patient’s unique circumstances and lifestyle needs.
Partial knee replacement is less invasive but provides faster recovery, but for only a select number of patients. Total knee replacement is more complex and often used and provides long-term relief to patients with advanced joint illness.
A careful examination and discussion with your orthopaedic surgeon will determine the ideal solution. Taking the correct decision will restore freedom of movement, rid you of pain, and enable you to lead a satisfying, active life again.